A recent report by PR Newswire indicates that in 2020 alone, 90% of hospitals utilized Artificial Intelligence (AI), representing a 37% rise from 2019. With global healthcare spending reaching $8.8 trillion, providers are looking for new ways to tap into this massive market. Consequently, the global data automation in the healthcare market is expected to reach $88.9 billion by 2028. Data automation is the process of using technology to handle repetitive data tasks, and companies providing healthcare software services to boost this automation are in high demand.

Even before the pandemic, providers viewed automation as the next step in delivering high-quality services. Data automation helps organizations manage the lifecycle of information from data collection to final analysis. In this context, let’s dive deep into a comprehensive overview of data automation in healthcare, investigating use cases of data automation and the benefits of data automation.
Are you finding managing complex data as a bottleneck for your clinical excellence? Contact SPsoft to discover how our custom data integration solutions and intelligent data pipelines can streamline your operations and enhance patient outcomes!
Table of Contents
When to Know Automation is Needed?
Dealing with large volumes of data and engaging in numerous administrative tasks takes a significant amount of time. Organizations are becoming more complex, and data teams, including the data engineer and data scientists, are often overloaded. Burnout becomes a reality when staff deal with repetitive, manual data handling.

Data organization software and a robust data automation tool become vital if an organization experiences backdrops in data preparation or data handling. Almost every healthcare provider experiences problems with repetition, meaning nearly everyone can benefit from implementing data automation. To harness the potential of data, you must move away from archaic manual entries and toward an automation tool that can process and analyze data with precision.
What is Intelligent Data Automation?
Intelligent Data Automation is the application of techs directed at efficient decision-making. The automation process is delivered through Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Business Process Management (BPM). Forbes indicates that Intelligent Automation is crucial for boosting business performance and revolutionizing the business world.
RPA
RPA is a core component of data automation. It involves robots engaging in back-office operations like data loading and data extraction. When coupled with a sophisticated data pipeline, RPA can process vast amounts of data that require deep analysis. IBM suggests that RPA, when integrated into a broader data strategy, brings seamlessness to health ecosystems.
AI and Machine Learning (ML)
AI is one of the well-recognized technologies associated with automation. AI algorithms mimic human reasoning to analyze data. ML uses these outputs to translate them into real-time data predictions. Both tools rely on historical data to improve data quality and provide predictive analytics. Reliable data is the foundation for these models to work effectively.
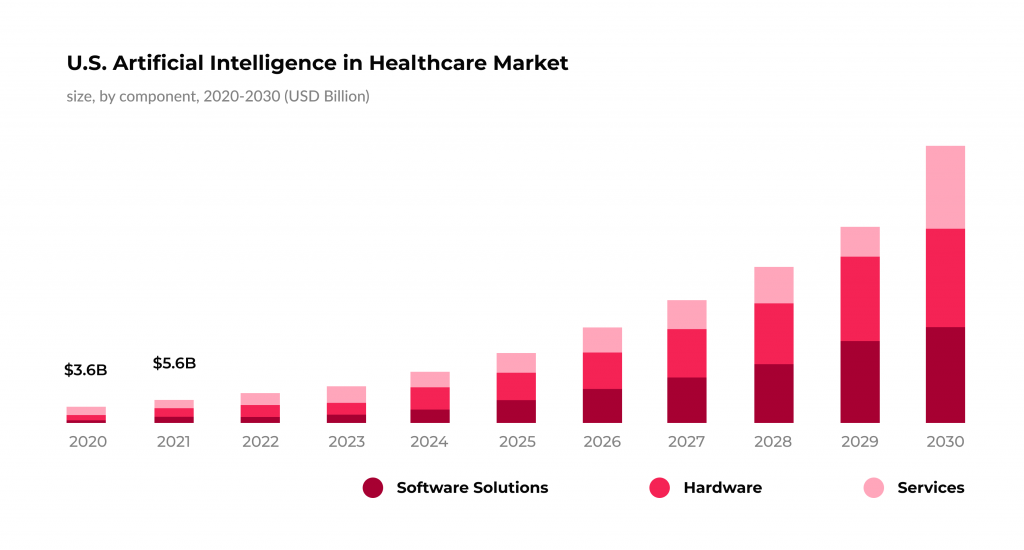
Deloitte argues that harnessing the power of AI and ML is a direct way to bring automation and analytics into data management, and the numbers above prove that. Thus, AI and ML services integrated into healthcare open new horizons for running top-notch data management systems.
BPM
BPM streamlines data workflows and business processes. It ensures that the automation process improves the reliability of multiple procedures. In healthcare, BPM is vital as it brings responsiveness to ecosystems, allowing a data engineer to optimize data flow between departments. Here is a list of some most recognized BPM platforms on the market.
Semantic Software Systems
When turning to auxiliary technologies, the ones often used with RPA, BPM, and AI, one should start with semantic software systems. The sufficient scholarly evidence points out that semantic model-driven frameworks bring the Semantic Web closer to businesses and organizations, thus allowing a higher degree of interaction with clients, customers, and patients.
Simply put, semantic systems make machines and algorithms better understand data. This instrument uses Web Ontology Language (OWL) and Resource Description Framework (RDF), which enhances data accessibility and precision.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Better healthcare automation is brought by NLP as well. While part of AI and closely related to linguistics, these tools within Intelligent Automation focus on understanding human language, allowing data teams to process vast data volumes found in clinical notes and unstructured data. Harvard Business Review coins NLP as the next massive breakthrough in AI. Respectively, the tech helps better understand patient needs and improve the quality of user-provider interaction.
Computer Vision
Computer vision is a part of AI allowing machines and algorithms to extract relevant raw data from different digital sources. They include images, videos, and other visual-based inputs. After processing such information, computer vision software offers recommendations and assists in decision-making. NVIDIA sees computer vision as having multiple applications in commercial and noncommercial industries. In healthcare, computer vision can be integrated when working with mHealth and telemedicine. Therefore, you can develop a video calling app and enhance it with computer vision.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
OCR is a technology that translates handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, helping to transform data from paper records into a digital data lake. Amazon suggests OCR can be important when converting your workflow from paper to digital. Within healthcare automation, OCR can help with paper forms, receipts, and images linked to Personal Health Information (PHI). In other words, with OCR, you get more efficient data management systems.
Administrative Applications
Data organization software includes an array of different administrative applications. That correlates to the introduction of AI and is linked to more efficient workflows with few human errors. For instance, administrative applications help deal with Revenue Cycle Management (RCM), reports, and any clinical-related paperwork. These applications help optimize administrative tasks and present up-and-running solutions for data management.
Rule-Based Expert Systems
Rule-based expert systems help facilitate decision-making. Essentially, professionals take outputs from processed data and set hardcoded principles about aspects like prognosis or treatment. A broader perspective on such systems show how properly coded rules can bring automation closer to prognosis, making healthcare staff’s work easier and more seamless.
While reliant on AI, RPA, and BPM at its core, there are additional tools that help reveal the true potential of intelligent automation. Yet, plunging further into the case, one should determine whether data automation in MedTech is worth considering in the first place.
Healthcare Data Automation Importance
The importance of data automation is visible through its massive market size. For a data engineer, creating a data pipeline that can integrate data from different data sources is no longer a luxury — it is a competitive necessity.

Eligibility, Claims, and Billing
Eligibility checks and authorization are time-consuming processes requiring plenty of dedicated resources from healthcare providers. Moreover, when handled by human agents, these areas are prone to a high chance of error. Bringing AI and RPA as a part of Intelligent Automation is key for changing such a scenario. It grants more optimization and secured access to insurance information and electronic medical records (EMRs). After all, any error can be extremely costly in terms of organizational and patient outcomes.
With the rising number of patients and the growing healthcare industry, the difficulty of status administration increases correspondingly. However, automated data systems submit and process claims seven times faster than humans. After the claim is processed, the automation is used to monitor and update statuses at predetermined intervals. Also, top healthcare software companies integrate alerts linked to claims to indicate when human involvement is needed.
Finally, one can expect medical billing to be complex and overbearing. Even when working with a single patient, there is a massive paper or digital trail linked to billing information at some point. Extracting and analyzing data from these procedures can be invaluable. However, it can take a massive chunk of time and resources when done manually or with outdated algorithms. Data automation allows AI coupled with OCR to load data from patient records directly into billing systems, reducing manual data handling errors and speeding up the invoicing process. By implementing data automation, organizations ensure data accuracy in insurance information.
Registration, Scheduling, and Appointment Reminders
For decades, healthcare professionals have used Electronic Health Records (EHRs), a staple for handling registration. While EHRs have been used for years, data automation offers the ability to update these records in real-time. For administrative staff, automation makes data entry more organized and optimized. In such a case, if you consider developing or updating your EHR platform, always keep the automation factor in mind.
Appointment management software rooted in automation makes the entire process more efficient. Intelligent Automation can accurately show how many patients are seeking medical attention and correlate it to the number of physicians available to offer services. From a patient’s perspective, appointment schedules have always been an issue. Fortunately, automation enables patients to book, cancel, and confirm appointments without human intervention.
MGMA indicates that automated appointment reminders are used by about 88% of healthcare organizations. The number should grow, and the underlying technology can boost customer satisfaction with the care provided. Data organization software helps organizations avoid no-show appointments while helping the patient arrive for a physician visit on time.
Check-Ins, Informed Consent, and Referrals
Healthcare data engineering aided with automation brings the effectiveness of patient check-ins to another level. For example, medical staff can automatically analyze past visits and check-ins to fill out forms during patients’ future visits. In such a case, automation helps streamline data and ensures that accurate data is available at every touchpoint of the data lifecycle.
Meanwhile, informed consent is vital for delegating multiple procedures within healthcare provision. It can affect administrative workflows and patient outcomes. Bringing healthcare automation to deal with informed consent optimizes the process of data collection. It is essential because physicians and administrators can have tools that illustrate patient opinions, especially those corresponding to their consent. So, when the factor of informed consent is considered, it grants physicians and other healthcare professionals more time to deal with high-priority tasks.
Lastly, as a health system expands, it will experience a growing number of recurring contracts. Managing these requires time and human resources. Importantly, if a provider cannot deal with contracts efficiently, it will face a financial loss and hectic organization of internal processes.
Healthcare automation brought by AI presents solutions allowing rapidly scanning contracts to extract vital data. Automation software can handle multiple contracts at once and compare the information. It results in better risk analysis and more effective supply management.
Data Migration and Integration
Although EHRs have been used by healthcare organizations for decades, the evidence shows a bit of stagnation in the EHR market.
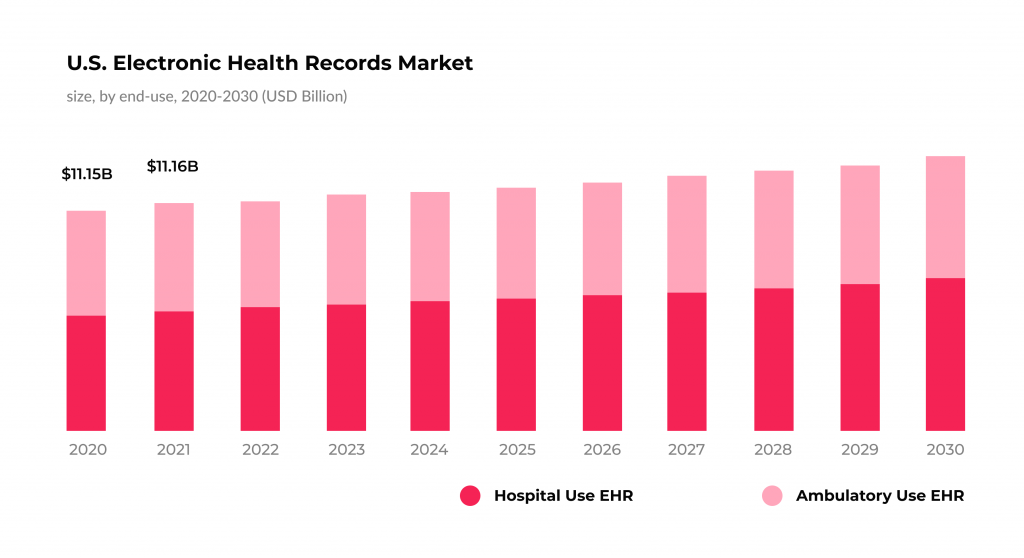
While EHRs still help handle aspects like data migration, the more information these systems encounter, the higher the likelihood of errors and inefficiencies. Thus, it is vital to find a way to make them more accurate and effective or find substitutes that will address the increasing pressure of data flows. Even a more tremendous issue arises during data migration. If you need to move datasets from one system to another, you may face challenges EHRs cannot resolve.
Moving multiple data sets between legacy systems and modern data warehouses is a common example of data automation. Data automation work in this area involves using RPA to move data without records being left behind. A data engineer uses data transformation to ensure that when data is loaded, it meets the high-quality data standards of the new system.
Data Automation in Healthcare Use Cases
Proper healthcare automation can mean the difference between commercial success and failure, with patient outcomes being a factor to consider. Without further ado, let’s deconstruct several use cases increasing the worth of data automation in healthcare.
Use Case #1. Consolidating Data from Multiple Sources
At this point, we see that RPA plays a leading role in delivering the advantages of Intelligent Automation. This assumption can be supported by the evidence of RPA’s growing market size.

RPA gained its trust through its ability to handle different types and volumes of data. Health data comes from data from various sources, including third-party portals and scheduling systems. At the same time, that may involve different data sources like insurance vendors or health record databases. Often, the data stream is decentralized and relies on healthcare organizations utilizing massive resources to collect, store, and analyze it.
RPA and data integration tools have proven to play a central role in efficiently processing health data. According to LexisNexis, they can collect and analyze data without the $2.1 billion loss typically associated with human error in data handling.
Use Case #2. Monitoring Assets with Real-Time Data
Data automation work in MedTech can help track assets effectively, improving patient outcomes and reducing the financial losses linked to incorrect asset management. After all, each hospital has instruments like medical pumps, ventilators, and defibrillators.
Those particular tools were of their utmost importance during the COVID-19 pandemic when the incorrect asset management stretched and thinned resources. That makes appropriate asset tracking extremely significant. Staggeringly, it is estimated that nurses spend about 6,000 hours per month looking for lost assets. In a time of urgency, the inability to find equipment can drastically affect patient outcomes.
By using sensors and data automation tools and technologies, hospitals can manage data regarding equipment locations, saving nurses thousands of hours of searching. With these technologies, thousands of hours will be saved, and medical professionals will have immediate access to life-saving equipment at a moment’s notice.
Use Case #3. Diagnostics and Data Quality
The advantages of data analytics in healthcare have a direct impact on the effectiveness of diagnostics. So, the inability of healthcare providers to collect and analyze vast amounts of patient data results in incorrect predictions and unsupported credible evidence diagnostics. This scholarly source suggests a 0.7% diagnostic analytics error among all admissions.
Take the COVID-19 admissions in 2021. There were an estimated 32 million admissions in a year. With 0.7% of admissions affected by diagnostics error, it results in 224,000 patients being affected. Data automation tools can help decrease the percentage of diagnostic errors, thus reducing the number of misdiagnosed patients.
By using a data automation tool to process and analyze data from admissions, providers can ensure data integrity and reduce misdiagnosis. High-quality data is essential for mHealth and telehealth accuracy.
Use Case #4. Offering Customer Service
About 84% of patients appeal to online reviews to assess physicians. Therefore, customer service plays a leading role. Having a customer service department can be a costly endeavor. Besides, making administrative staff serve as customer support can cost precious time that could have been used to improve patient outcomes.
Intelligent Automation brought to healthcare services tools like AI voice agents and AI-powered chatbots. They can dramatically reduce the workload of human agents and almost completely substitute the entire customer support department. They bring the following aspects:
- human-like patient interaction
- 24/7 support
- appointment reminders
- automated appointment rescheduling and canceling
- valuable information extraction
Data management systems integrated into customer service reduce the number of no-shows, boost customer satisfaction, and improve the patient experience with round-the-clock support. Ultimately, they help increase healthcare employees’ productivity by relieving them from mundane customer service tasks.
Use Case #5. Compliance with Rules and Regulations
Companies operating with patient data must comply with specific rules and regulations, and one of the critical standards is HIPAA. It protects PHIs and ePHI and ensures medical organizations have procedures helping to handle patient data securely. HIPAA violations result in massive penalties. On average, a company can pay a $60,000 fee for noncompliance. In some cases, the number is as high as $1.9 million.
With Intelligent Automation, it is possible to boost compliance. AI-powered instruments allow healthcare providers to have systems automatically tracking every authorization and logging. You see who is using patient data and what for in real-time. That increases transparency and ensures compliance. As a result, Intelligent Automation helps companies avoid hefty fines associated with noncompliance and allows using HIPAA-compliant software from the get-go.
Use Case #6. Top-Notch Health Analytics
Intelligent Automation brings forward advantages of data analytics healthcare. Equipped with data organization software, healthcare providers can run AI-powered analytics to improve different health and operational processes. The National Health Care Anti-Fraud Association estimates that fraud in healthcare costs about $68 billion annually. Thus, automated solutions help detect malicious activity and use analytics to avoid fraud and breaches.
Moreover, the power of predictive analytics in healthcare brought by AI and ML can boost data security, enhance treatment planning, and provide more accurate anticipations from drug trials. While data automation in MedTech is not a panacea, it can drastically reduce the chance of fraud being committed, which saves healthcare organizations plenty of finances.
Benefits of Hospital Data Management for Administrators
When speaking about some other benefits data management systems bring to administrators, these are the ones to mention:

- Higher task optimization. RPA enables administrators to handle numerous administrative tasks, which takes a massive workload from staff, allowing them to focus on more high-priority tasks.
- Greater staff support. Data management systems boost staff support by automating tools like triage screening and self-diagnosing. It helps the staff to avoid doing mundane tasks, the ones that patients can handle themselves.
- Seamless patient communication. Chatbots and AI voice agents use NLP and AI to provide human-like communication to consumers. For instance, administrators can take the bearings of customer service from the staff and let them handle more pressing tasks.
- Top-grade data security. Intelligent Automation brings forward technologies like blockchain. It enables bank-grade encryption and data security that changes how healthcare leaders use and work with patient data to improve care.
- Intuitive dashboard analytics. Health administrators constantly deal with tasks directed at improving operational efficiency. Dashboards clearly define all the KPIs to guide the decision-making process. Data management systems come with interactive dashboards offering insights from AI-powered algorithms, which means the ones with high precision.
- Rapid data transfer. When a healthcare organization decides to improve its operations, it entails a lot of changes. For instance, a healthcare provider wants to shift from paper to digital forms to improve access to patient data. Tools like OCR can be done seamlessly and with a low chance of error. In general, healthcare automation makes data migration and innovation more accessible.
These are the benefits healthcare leaders and administrators can get from Intelligent Automation adopted in healthcare. With the increasing number of healthcare data engineering use cases, one should expect more advantages of unraveling the phenomenon.
Benefits of Healthcare Automation for Patients
The entire healthcare industry works to improve patient outcomes. If your healthcare software creates consumer value, it will succeed. At this point, there are particular patient-based benefits brought by healthcare automation:
- Fewer medical errors. Medical errors can cost between $4 billion and $20 billion. More importantly, they cost lives. Healthcare automation brings more accurate analytics, which helps better understand patient data and reduce the number of errors made.
- More accurate diagnoses. Automation can boost clinical decisions while also supporting evidence-based practice. In addition, while diagnosing is time-consuming, automation can speed up the process, thus reducing the chance for patients to experience worsening symptoms due to diagnosis delay.
- Internet of Things (IoT). The booming IoT market brings new opportunities to improve patient outcomes. Automation coupled with wearable medical devices delivers care outside a hospital. It enables physicians to track patient data and identify diseases at the early stages of their development.
- Superior patient care. Data organization software enables providers to offer highly personalized care and around-the-clock support. It leads to a better consumer experience and higher quality of care delivery.
- Easier maintenance. With automation, patients can get their test results much faster. With fewer manual machines being used, there are growing opportunities to decrease the reliance on delicate equipment. Besides, patients can use automation software to get their needed information without communicating with physicians.
The pros above make healthcare automation an invaluable tool for improving care delivery and patient outcomes. However, as with every new tech or instrument, specific challenges exist. Automation tecрs are still developing, and some issues are revealed through trial and error.
Key Takeaways
Long story short, automation offers various benefits for healthcare. Besides, there are existing use cases suggesting the advantages are not only theoretical but also tangible. With the global healthcare automation market booming further, it is a matter of time when there will be no single healthcare provider able to pass on the option to adopt automation tools.
The future of healthcare automation is bright. Yet, you should not look at the automation through rose-tinted glasses. There are always factors like security and compliance to consider at all times. Prepare for the transition. Have sufficient funds and make sure your staff knows what is to come. Choose automation software carefully and have the checklist we mentioned before. After all, the final saying about whether automation will bring patient value is always after you.
Are you considering the transition to automated workflows? Contact SPsoft to develop a data automation strategy that protects patient privacy, maximizes efficiency, and turns your raw data into actionable clinical insights!
FAQ
What is the primary role of a data engineer in healthcare automation?
In the context of healthcare, a data engineer is responsible for designing, building, and maintaining the data pipeline that allows information to flow securely between systems. They ensure that data integration is seamless, allowing the organization to integrate data from different data sources such as EHRs, lab results, and pharmacy records. The data engineer also performs data transformation to convert raw data into a format suitable for data analysis, ensuring that the data quality remains high throughout the entire data lifecycle.
How does data automation help improve data quality in clinical settings?
Data automation helps improve data quality by eliminating the inconsistencies and errors inherent in manual data handling. An automation tool can perform data validation in real-time, ensuring that data entry meets specific standards before it is saved to a data warehouse. By using data automation strategies, healthcare providers can ensure data integrity and maintain accurate data across multiple data silos. This reduction in human error ensures that reliable data is the foundation for all clinical decisions and patient outcomes.
What are the main data automation challenges in the MedTech industry?
The most significant data automation challenges include ensuring data security and patient privacy while maintaining a seamless data flow. Implementing data automation can be costly, and organizations often face resistance to innovation from staff accustomed to traditional data processes. Furthermore, data silos and different types of data make data preparation and data integration complex. A successful data automation process must address these hurdles by establishing clear data governance and a robust data strategy.
Can you provide an example of data automation in a hospital’s administrative workflow?
A common example of data automation is the automated processing of insurance claims. Instead of a human agent manually entering data, an automation tool using OCR and AI can extract data from medical documents and load data directly into the billing system. That enables the organization to process claims seven times faster, effectively using technology to handle repetitive data tasks. This streamline data approach not only saves time but also reduces the financial risks associated with manual data handling errors in the revenue cycle.
What is the difference between a data lake and a data warehouse in healthcare?
A data lake is a storage repository that holds a vast amount of raw data in its native format until it is needed, which is ideal for storing unstructured data like medical images. Conversely, a data warehouse is a database optimized for data analysis, where data is loaded after undergoing data transformation to fit a specific schema. Data automation tools can help move information between these two, ensuring that the data engineer can manage data efficiently to support both research in the data lake and operational reporting in the data warehouse.
How does data automation work with real-time data from wearable devices?
Data automation work with wearables involves creating a data pipeline that can ingest and process vast amounts of data from IoT sensors. Data automation offers the ability to analyze data instantly, alerting physicians if a patient’s vitals deviate from the norm. This real-time data flow requires sophisticated data integration to ensure the information is correctly mapped to the patient’s record. By using automation solutions, providers can harness the potential of data to provide care outside the hospital, essentially extending the data lifecycle to the patient’s home.
Why is data validation important in the data automation process?
Data validation is a critical step in the automation process because it ensures that the data is loaded correctly and without corruption. Data automation tools use validation rules to check data formats and data types for consistency. Without this step, vast amounts of data expose the system to “garbage in, garbage out” scenarios where incorrect raw data leads to faulty clinical predictions. By incorporating data validation into the data pipeline, the data engineer can maintain high-quality data that clinicians can trust.
How do data automation tools help in data migration between EHR systems?
Data automation tools like RPA and OCR streamline data migration by automating the data movement from a legacy EHR to a new platform. These automation systems ensure that large volumes of data are moved with high data integrity, ensuring that no patient records are left behind. The automation process also handles the data transformation needed to map old data models to the new system’s requirements. This reduces the time and cost of migration while preventing the human-made errors that often occur during manual data handling.



