Healthcare is rapidly evolving, embracing technology to boost efficiency, enhance patient outcomes, and control costs. A key player in this transformation is the AI agent healthcare system. These are intelligent systems that learn, adapt, and make decisions, leveraging techs like machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) to analyze diverse data sources, including electronic health records (EHRs) and patient monitoring data.
Why is there a growing interest in the healthcare AI agent? The potential advantages are significant. Organizations see improved operational efficiency as agents automate tasks 24/7, potentially cutting operating costs by 20-40%. These agents also enhance patient outcomes by offering clinical decision support and enabling proactive monitoring, reducing diagnostic errors. Besides, administrative functions see gains, with reports of 30-50% increases in throughput.

The market reflects this dynamic. The global AI in healthcare market was valued at $26.69 billion in 2024, projected to hit $36.96 billion in 2025, and potentially exceed $613 billion by 2034 (36.83% CAGR). Adoption is widespread: 86% of medical organizations report extensive AI use, and 75% explore Generative AI. By 2025, 90% of US hospitals are expected to use AI for functions like early diagnosis. Gartner predicts that 33% of enterprise software will feature agentic AI by 2028. This growth is driven by digitization, wearable data, chronic disease burdens, and the need to address staff shortages and improve value-based care.
The blend of market opportunities and adoption challenges highlights why defining requirements is critical for any AI agent for a healthcare project. Meanwhile, the rise of more autonomous, “agentic” AI further emphasizes the need for precision, defining not just tasks but also the limits of autonomy. And finally, the focus on ROI means demonstrating value through clear metrics, which must be part of the requirements process.
Ready to benefit from the power of AI agents in your healthcare setting? SPsoft has the expertise to help you define requirements and build effective, compliant solutions. Contact us today!
Functional Needs: What Should Your AI Agent for Healthcare Do?
Defining functional requirements clarifies what a healthcare AI agent must achieve. The needs of AI agents in healthcare use cases differ greatly, from administrative tasks to clinical support.
Understanding the Language of Medicine
A core requirement for many AI agent healthcare applications is accurately processing medical language, including complex terms, abbreviations, and clinical jargon in unstructured text like EHR notes.
- Requirement. The agent must be highly faithful in understanding medical language to prevent misinterpretations that lead to errors.
- Techniques. That relies on advanced NLP and Understanding (NLU). Often, models need specific pre-training or fine-tuning on biomedical data (BioBERT, ClinicalBERT). Mapping terms to standardized ontologies like UMLS or SNOMED CT is also vital.
- Importance. Accurate NLP enables reliable data extraction, understanding of patient queries, and effective communication with professionals.
Enabling Seamless Conversations
Many AI agents for healthcare roles involve direct interaction, necessitating natural, coherent, and context-aware conversational abilities.
- Requirement. The agent must engage naturally via text and voice, maintaining context throughout dialogues.
- Capabilities. Beyond basic Q&A, it should handle complex queries, provide clear explanations, offer guidance, and exhibit empathy. Voice interaction enhances accessibility, requiring technical accuracy and practical communication skills.
- Example Use Cases. Powers virtual health assistants, chatbots for FAQs or guidance, and clinician assistants for data retrieval or summarization.
Automating Core Processes
Automation is a major driver for adopting AI agent healthcare solutions.

Intelligent Appointment Scheduling & Reminders
- Requirement. Agents should perform symptom-based triage, assess urgency, route patients, automate scheduling, and send reminders to minimize no-shows.
- Benefit. Addresses access issues, reduces wait times (up to 30% reported), optimizes schedules, cuts missed appointments and improves patient flow.
Streamlining Patient Queries & Intake
- Requirement. Act as the first contact for routine questions and assist with patient intake, gathering demographic and preliminary health data via conversation.
- Benefit. Reduces staff workload, improves data accuracy, and enhances the patient experience.
Handling Administrative Overhead
- Requirement. Automate back-office tasks like billing, insurance verification, claims, medical coding, and inventory management.
- Benefit. Improves accuracy, reduces errors, increases throughput (30-50% gains reported), and saves staff time.
Augmenting Clinical Capabilities
AI agent applications in healthcare are increasingly supporting clinicians.
Providing Non-Diagnostic Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
- Requirement. Analyze complex data (EHRs, imaging, genomics, real-time monitoring) to identify risks, highlight patterns, summarize literature, and suggest potential pathways. Crucially, agents provide support, not definitive diagnoses or decisions, which remain the clinician’s responsibility.
- Benefit. Enhances diagnostic accuracy, supports personalized treatment plans, and improves patient safety.
Enhancing Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
- Requirement. Integrate with wearables/sensors to analyze real-time physiological data, detect anomalies, generate alerts, and suggest interventions based on protocols.
- Benefit. Enables proactive care, especially for chronic conditions, potentially reducing complications and readmissions.
Ultimately, requirements must be tailored to the specific application and users (patients, clinicians, administrators).
How to Integrate Your Healthcare AI Agent Seamlessly
Functional capabilities depend on the healthcare AI agent operating within the existing tech ecosystem. Technical requirements define connections to data sources, communication with other systems, and workflow integration. Seamless integration is key to realizing the value of AI agent applications in healthcare.
Connecting to the Core: EHR Integration (Epic, Cerner, etc.)
The EHR is central to patient information. Seamless, often bidirectional, integration with major EHRs (Epic, Cerner, Allscripts) is critical for most clinical AI agent healthcare solutions.
- Requirement. Securely access relevant EHR data (history, meds, labs, notes) for context and potentially write back information (summaries, alerts, appointments).
- Methods. Primarily through APIs, especially FHIR-compliant ones, SMART on FHIR provides secure authorization. Older systems might use vendor APIs or HL7 messages. Integration platforms can simplify connections.
Ensuring Interoperability: The Role of HL7 and FHIR Standards
A healthcare AI agent must often interact with various systems (LIS, RIS, pharmacy, devices). Adherence to interoperability standards is essential for reliable data exchange.
- Requirement. Understand and exchange data using established standards for consistency and accurate interpretation.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). The leading modern standard using RESTful APIs, making integration easier. Defines data in modular “Resources” (Patient, Observation) for granular access. Preferred for new AI agent healthcare integrations due to flexibility and real-time capabilities.
- HL7 (Health Level Seven). Older, established standards (v2, v3/CDA) are still widely used. They can be more complex than FHIR. Agents might need to handle HL7 messages (often via middleware) for legacy system interaction. Many environments require hybrid strategies.
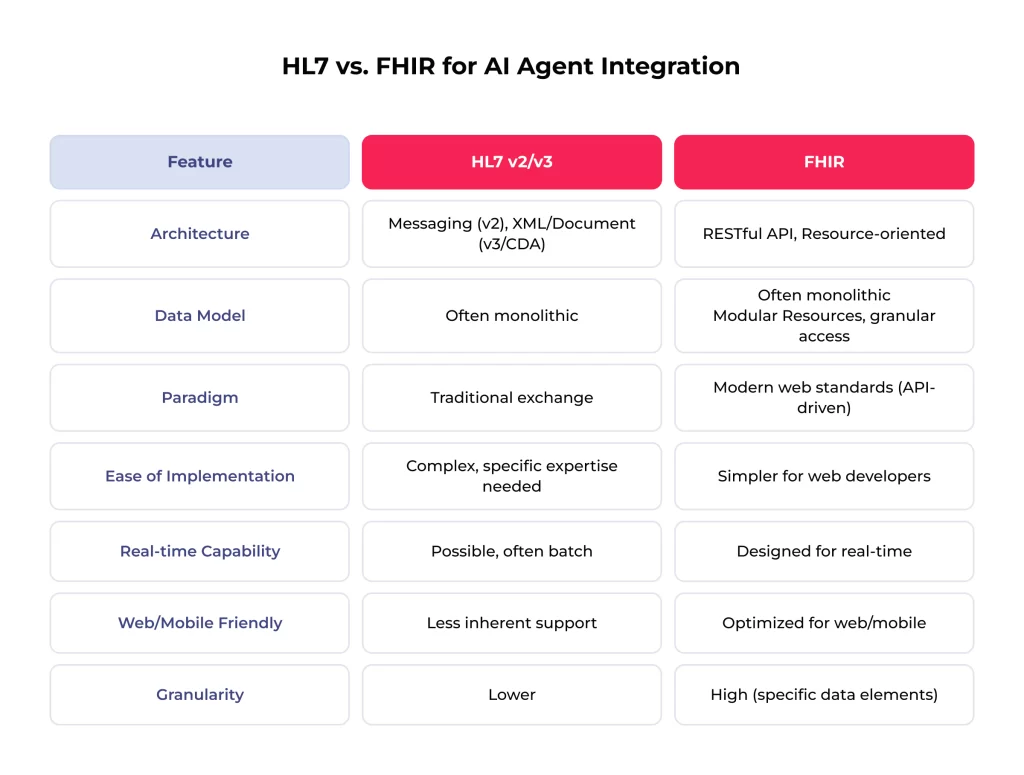
FHIR is generally favored for integrating modern applications like healthcare AI agents due to its flexibility and ease of use.
Fitting into the Workflow: Integration with Apps, Portals, and Call Centers
Technical connection is not enough; the healthcare AI agent must integrate smoothly into users’ existing tools and processes for adoption.
- Requirement. Functions must be accessible within existing applications (patient portals, clinician dashboards, telehealth, call center software) without disrupting workflows.
- Methods:
- APIs. Agent exposes APIs for existing apps to call.
- Embeddable Components/SDKs. Pre-built UI elements or SDKs for easy embedding.
- Chat Interfaces. Integrating chat widgets into portals/apps.
- Backend Integration. The agent operates behind the scenes, triggered by system events.
- SMART on FHIR Apps. Launched directly from the EHR.
- Call Center Integration. CTI links or platform APIs for call routing, transcription, etc.
Requirements must specify technical connections and user experience aspects, such as trigger points, information presentation, user interaction, and output consumption.
Security and Compliance for AI Agent Applications in Healthcare
Because of the sensitivity of health data, security and compliance are non-negotiable for any AI agent healthcare system. Building trust requires rigorous data safeguarding and adherence to regulations like HIPAA, which are integrated from the start.
Navigating HIPAA: Ensuring Regulatory Adherence
In the US, HIPAA sets the standard for protecting Protected Health Information (PHI). Compliance is mandatory for any AI agent handling PHI in healthcare.
- Requirement. The agent and infrastructure must comply with HIPAA Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules via administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs). Legally required when using third-party AI vendors accessing PHI, outlining vendor responsibilities and liability. Verifying vendor willingness/ability to sign a BAA is a key requirement.
- AI for Compliance Monitoring. AI can enhance compliance by monitoring logs, detecting violations, automating audits, and classifying data.
Protecting Patient Data: Key Security Measures
The HIPAA Security Rule mandates technical safeguards for electronic PHI (ePHI). Key requirements for a healthcare AI agent include:
Encryption and Secure Storage Protocols
- Requirement. All PHI must be protected with strong encryption, both at rest (storage) and in transit (networks), using industry standards (e.g., TLS 1.2+). Data must be stored on secure, HIPAA-compliant infrastructure.
Implementing Robust Access Controls
- Requirement. Access to PHI must follow the principle of least privilege, typically using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) offers more granularity. Strong authentication (e.g., MFA) is essential.
The Importance of Detailed Audit Logs
- Requirement. Comprehensive, immutable audit logs must record all PHI-related events (creation, access, modification, transmission). These are vital for monitoring, incident investigation, and demonstrating compliance. AI can analyze logs for anomalies.
Other Security Considerations
A comprehensive security posture should also include:
- Data Minimization & De-identification. Collect/retain minimal PHI. Use de-identified or anonymized data where feasible (for training, analytics), potentially using techniques like differential privacy.
- Secure Development Lifecycle. Embed security throughout development (secure coding, vulnerability scanning, testing).
- Regular Audits & Risk Assessments. Conduct periodic independent audits and risk assessments.
- Incident Response Planning. Maintain a clear response plan for security incidents and breaches.
Achieving robust security and compliance requires a holistic approach combining technology, process, and governance.
Tailoring and Scaling: Customization and Performance Requirements
An effective AI agent healthcare solution must be adaptable to specific contexts and perform reliably under real-world conditions. Customization ensures relevance and performance metrics validate effectiveness and scalability.
Customizing for Medical Specialties and Departments
- Requirement. Agents often need tailoring to the unique terminology, protocols, and workflows of different specialties (cardiology, oncology) or departments (emergency).
- Methods:
- Specialized Training Data. Using domain-specific datasets.
- Fine-tuning. Adapting large models with smaller, specialized datasets.
- Knowledge Integration (RAG). Accessing curated knowledge bases (guidelines, research) in real-time.
- Workflow & Logic Configuration. Customizing decision logic and conversational flows. Requires mechanisms to update knowledge as guidelines change.
Bridging Language Barriers & Adhering to Local Guidelines
- Requirement. Support multiple languages for equitable access. Operate according to local medical guidelines, standards, and regulations.
- Methods. Multilingual support via NLP models trained on diverse data or machine translation (MT), potentially using multi-agent systems. Adherence to local guidelines via region-specific knowledge bases, training data inclusion, or specific prompting.
Achieving Accuracy in Real-world Healthcare Settings
- Requirement. Specify expected accuracy levels using relevant metrics, such as sensitivity, specificity, precision, recall, task completion rate). Accuracy must be validated in real-world clinical scenarios.
- Examples. AI achieving high accuracy in specific tasks like heart attack rule-out (99.6%) or diagnostic imaging (up to 20% improvement) has been reported.
Ensuring Scalability for High Interaction Volumes
- Requirement. Architect the system to handle anticipated interaction/data volumes efficiently and scale effectively without performance degradation.
- Considerations. Cloud-based deployment (AWS, GCP, Azure HIPAA services) and containerization (Kubernetes) often facilitate scalability.
Leveraging Analytics for Actionable Insights
- Requirement. Provide built-in analytics or generate data for external platforms.
- Insights. Analyzing interaction data yields valuable insights:
- Operational Efficiency. Time saved, tasks completed, wait time reduction.
- Interaction Analysis. Common queries, resolution rates, user satisfaction.
- Patient Sentiment Analysis. Understanding patient emotions (frustration, satisfaction) from conversations.
- Trend Identification. Patterns in patient needs, system bottlenecks, risks.
- Benefit. Enables data-driven optimization of the agent, workflows, user experience, resource allocation, and value demonstration. Crucial for validating accuracy and guiding improvements.
Final Thoughts
Successfully implementing an AI agent healthcare solution starts with defining its requirements across multiple dimensions:
- Functional (what it does)
- Technical (how it integrates)
- Security/compliance (how data is protected)
- Customization/performance (how it adapts and performs)
Defining these requirements meticulously is the strategic foundation for building effective, trustworthy healthcare AI agents. It aligns stakeholders, manages risks, and ensures the final product delivers tangible benefits.
The landscape of AI agent applications in healthcare is evolving towards more autonomous systems, multi-modal AI, and a greater focus on governance and ethics. These advanced agents hold immense potential to personalize care, improve outcomes, alleviate workforce pressures, and drive efficiency.
Navigating this requires expertise in both healthcare and AI. Defining requirements and building solutions for this demanding sector necessitates an experienced partner. SPsoft possesses the capabilities to guide healthcare organizations, ensuring healthcare AI agent initiatives are built on solid requirements and leading to compliant and value-driven implementations.
Partner with SPsoft experts to navigate the complexities of healthcare AI agent development and integration. Let’s build the future of AI healthcare effectively together. Reach out to us!
FAQ
What features should a Healthcare AI Agent have?
Features vary by application, but essentials often include:
– Strong NLP for medical terms
– Conversational abilities (text/voice)
– Task automation (scheduling, admin)
– EHR integration
– Non-diagnostic clinical decision support or monitoring
– Robust HIPAA-compliant security
Can the AI agent understand and process medical terminology?
Yes, this is fundamental. Effective agents use advanced NLP, often with models trained on biomedical text (BioBERT) and leveraging structured knowledge (UMLS) to interpret complex medical language accurately.
Does the AI agent support natural language conversations with patients or clinicians?
Many AI agent applications in healthcare (virtual assistants, chatbots) are designed for natural language interaction via text or voice, understanding intent and maintaining context.
Can the AI agent connect to EHR systems like Epic or Cerner?
Yes, EHR connectivity (Epic, Cerner) is critical. Integration primarily uses modern APIs, especially FHIR. SMART on FHIR is often used for secure app integration within the EHR.
Does it support interoperability standards like HL7 or FHIR?
Yes. FHIR is the preferred modern standard for an AI agent for healthcare integration due to its flexibility and API-first design. However, support for older HL7 standards may also be needed for legacy system compatibility.
Is the AI agent HIPAA-compliant?
HIPAA compliance is mandatory for agents handling PHI in the US. That requires technical (encryption, access controls, logs), administrative, and physical safeguards. Vendors typically sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
How is sensitive patient data secured and stored?
HIPAA requires encrypting PHI at rest and in transit. Access is strictly controlled (e.g., RBAC, MFA). Data is stored on secure infrastructure. Comprehensive audit logs track access. Data minimization/de-identification is used when possible.
How easy is it to customize the AI agent for different departments or specialties?
Customization is common and feasible, depending on the agent’s architecture. Methods include training/fine-tuning specialty-specific data, integrating knowledge bases (RAG), and configuring workflows and logic.
Can it support multiple languages or local medical guidelines?
Yes. Multilingual support uses NLP models trained on diverse data and MT. Local guidelines are incorporated via knowledge bases (RAG), training data, or specific AI instructions.
Does it offer analytics or insights based on conversations?
Yes, many platforms offer analytics. Insights include operational metrics, interaction patterns, and patient sentiment analysis, aiding performance monitoring and improvements.



